The WordPress memory limit, also known as the PHP memory limit, is the maximum amount of memory your site’s scripts can use. When your WordPress site runs many active plugins or hosts large media files, you might see these error messages while editing.
Fatal error: Allowed memory size of XX bytes exhausted.
Fatal error: Out of memory.
This error occurs when your WordPress code requires more memory than the default limit allows. But don’t worry; fixing this issue is simpler than you think, and you don’t need to be a tech expert to do it. Don’t let these errors hold you back; increasing your WordPress memory limit is a straightforward process that can keep your site running smoothly.
In this article, we’ll guide you through easy methods to boost your site’s memory limit. Whether you’re editing configuration files or using other tools, these steps will help you manage your site’s performance with ease. So, let’s dive in and explore how to increase your WordPress memory limit!
How Much Memory Does Your Site Need?
For most WordPress sites, a memory limit between 128 MB and 256 MB is typically sufficient. However, if your site is a resource-heavy beast—think e-commerce platforms or membership sites—you might need up to 512 MB.
It all depends on several factors:
- Traffic Volume: More visitors mean more server load, increasing memory usage.
- Plugin Count: The more plugins you have, especially resource-intensive ones, the more memory you’ll need.
- Media Complexity: Large media files like videos or high-resolution images can temporarily spike memory usage during processing.
By considering these factors, you can determine the right memory limit for your site and ensure it runs smoothly without hitting those dreaded memory limit errors.
How to Check Your Current Site Memory Limit
Before we dive into increasing your WordPress memory limit, it’s essential to know where you’re starting from. Here’s how we check our site’s current memory limit:
1. Log in to your WordPress dashboard.
2. Navigate to Tools > Site Health.
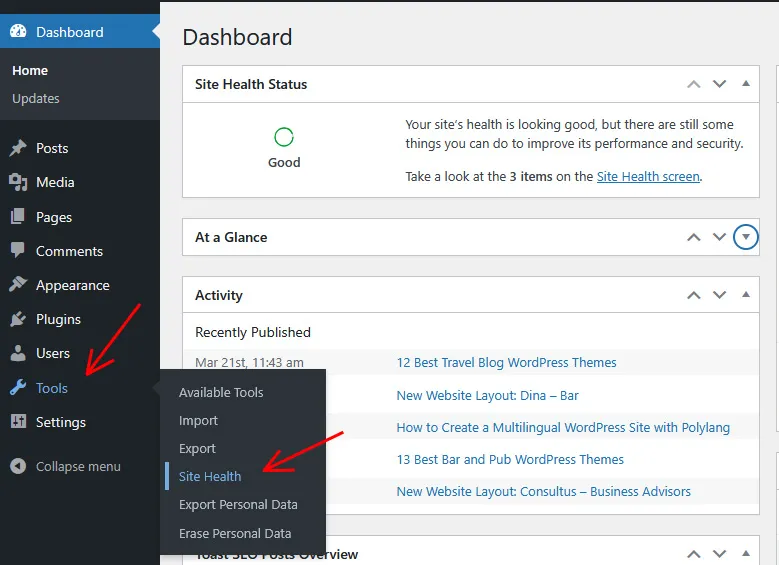
3. Click on the Info tab at the top.

3. Scroll down to the Server section and look for the PHP memory limit field. This will show you the current memory allocation for your site.

By following these steps, we can determine if our site is running on the default 32 MB or if it’s already been adjusted. Knowing this helps us decide how much more memory we need to allocate. Checking your current memory limit is a straightforward process that ensures we’re making informed decisions about our site’s performance.
How to Increase the WordPress Memory Limit – 2 Methods
Now, let’s get to the good stuff – increasing that memory limit! Before we dive into these changes, it’s crucial to ensure our site is backed up. Using a reliable backup plugin save us a lot of stress if anything goes wrong.
Here are two easy methods to help us boost our site’s performance:
Method 1: Edit the wp-config.php File
This is the most direct way to increase your memory limit. Access your site’s files using an FTP client like FileZilla or your hosting provider’s file manager. Locate the wp-config.php file in your site’s root directory ( public_html or www folders ). Backup the file before making any changes.
Open wp-config.php in a text editor and look for the line:
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '32M');If you find it, change the value to your desired limit (e.g., 256M).
If you don’t see this line, add it before the line that says “/* That’s all, stop editing! Happy publishing. */”:
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M');After saving and uploading the modified file, make sure to clear both your site’s cache and your browser’s cache. Then, head back to Site Health > Info > Server to verify if the php_memory_limit has increased as expected.
If you don’t see the change, it might be because your hosting provider doesn’t allow these modifications or automatically overwrites them. In this case, it’s best to contact your host and ask about their policies regarding memory limit adjustments. They can provide guidance on whether your changes are being overridden and suggest alternative solutions if needed.
Method 2: Edit the .htaccess File
Here’s how we do it:
Locate the .htaccess file: Use an FTP client to find it in your site’s root directory. Since it’s a hidden file, ensure your FTP client is set to show hidden files.
Backup the file: Before making any changes, download a copy of your current .htaccess file. This way, we can quickly restore it if something goes wrong.
Add memory limit rules: Open the .htaccess file in a text editor and add these lines at the end.
php_value memory_limit 256M
php_value upload_max_filesize 64M
php_value post_max_size 64M
php_value max_execution_time 300Make sure these new rules are placed after any existing WordPress rules.
Save and test: Save the changes and upload the file back to your server. Then, test your site to ensure everything is working smoothly.
If we encounter a 500 Internal Server Error, we should remove the added lines, restore the backup, and try smaller memory values.
Common Issues and Solutions
If you encounter problems after making these changes, there are a few things you can check. First, ensure that the file permissions are set correctly. For files like .htaccess, the permissions should typically be set to 644. This allows the server to read and execute the file while preventing unauthorized modifications.
If you checked the permissions and still can’t get to work, it might be because the hosting provider that doesn’t allow these modifications. Some hosts override custom settings or have specific requirements for editing configuration files. In this case, contacting your host is the best course of action. They can provide guidance on whether our changes are being overridden and suggest alternative solutions if needed.
Another common issue is encountering a 500 Internal Server Error after increasing the memory limit. This can happen if the new limit exceeds what your hosting plan supports. If you see this error, you should try reducing the memory limit to a smaller value and test again. For example, if you set it to 256M and get an error, you might try 128M instead.
Remember, if you’re still having trouble, reaching out to your hosting provider for assistance is always a good idea.
Conclusion
Increasing the WordPress memory limit is a straightforward process that can significantly improve your site’s performance. By following the methods outlined in this guide, you can easily boost your site’s memory allocation to handle more plugins, media, and traffic without running into those frustrating “memory exhausted” errors. Whether you’re editing the wp-config.php file, or updating the .htaccess file, these steps empower you to manage our site’s resources effectively.
If you encounter any issues, you can always revert to your site backups or reach out to your hosting provider for assistance. Remember, optimizing your site’s performance is an ongoing process, changing memory limits is just one part of maintaining a healthy and thriving WordPress site.